In the dynamic realm of medical manufacturing, the utilization of plastic injection molding stands as a cornerstone for crafting cutting-edge medical devices. This overview delves into the intricacies of medical injection molding, emphasizing its significance in meeting the high standards of precision and quality demanded by the medical device industry.
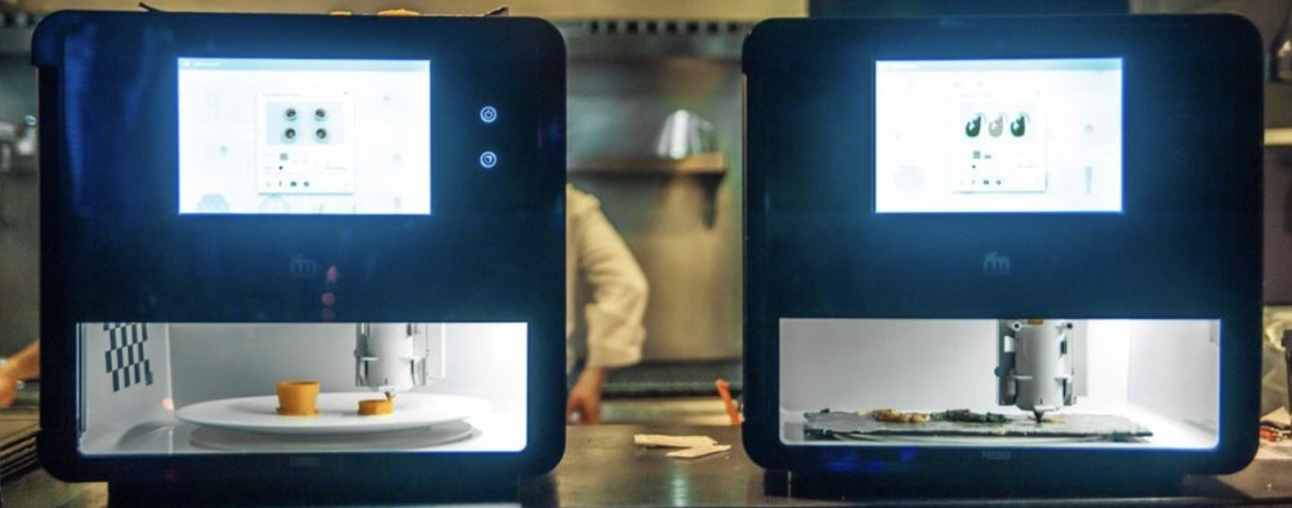
This s how 3d printing impacting the med field /* About to change */
At the heart of medical injection molding lies its unparalleled ability to deliver precision in the production of intricate medical components. This method ensures that each molded part meets exacting specifications, contributing to the creation of devices that demand utmost accuracy, such as surgical instruments and diagnostic equipment.
1. Precision Engineering for Critical Components: A fundamental advantage lies in the precision achievable through plastic injection molding. This method ensures the production of intricate and accurate medical parts, meeting the stringent requirements of critical applications, such as surgical instruments and diagnostic equipment.
2. Scalability and Efficiency: Plastic injection molding stands out for its scalability and efficiency in mass production. This section explores how this manufacturing process caters to the high-volume demands of the medical industry, ensuring consistent quality and timely delivery of medical components.
3. Material Selection for Medical Grade Compliance: The overview delves into the importance of material selection in plastic injection molding for medical applications. Highlighting the use of medical-grade plastics, it explores how these materials ensure compliance with stringent safety and regulatory standards, fostering the production of biocompatible and durable medical components.
4. Customization for Complex Medical Designs: The versatility of plastic injection molding enables the production of custom-designed medical components with complex geometries. This section examines how this capability allows manufacturers to tailor designs to specific medical applications, contributing to the advancement of specialized medical devices.
5. Cost-Effectiveness in Manufacturing: Cost-effectiveness is a key advantage explored in this overview. Plastic injection molding’s efficiency in material usage, reduced labor costs, and streamlined production processes contribute to overall cost savings. The section discusses how this cost-effectiveness benefits both manufacturers and end-users in the healthcare sector.
6. Consistent Quality and Regulatory Compliance: Ensuring consistent quality is paramount in the medical field. The overview delves into how plastic injection molding incorporates rigorous quality control measures, ensuring each medical part complies with regulatory standards. This section underscores the importance of meeting stringent quality benchmarks in medical component manufacturing.

Essential Requirements of 3D Printing in the Medical Field
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare, the utilization of 3D printing has become paramount, addressing crucial requirements that significantly impact patient care, design efficiency, and cost-effectiveness. Explore the fundamental requirements that position 3D printing as an indispensable solution in the healthcare industry.
1. Customization for Individualized Healthcare: The individualized nature of healthcare demands tailored solutions, making 3D printing an ideal fit for the industry. Instead of mass-producing identical parts, 3D printing empowers the creation of prosthetic and orthotic devices custom-fitted to a patient’s specific anatomy. This level of customization enhances the effectiveness of medical interventions, catering to the unique needs of each individual.
2. Leadtime Reduction for Critical Situations: Traditional manufacturing processes often involve long and costly lead times, posing potential threats in critical healthcare situations. 3D printing emerges as a solution, providing designers and engineers with the tools to rapidly create and iterate designs. This agility not only expedites prototyping but also facilitates effective communication with realistic prototypes. The ability to quickly implement design improvements based on direct feedback from medical professionals accelerates the overall design development process.
3. Cost-Effective Iterations and Production: Creating custom parts and devices requires meticulous detail, and manual processes carry the risk of human error, impacting costs and timelines. 3D printing mitigates this risk by enabling multiple iterations before the final product is printed. This iterative process helps identify and rectify potential errors, ensuring the end product meets the highest standards. Additionally, 3D printing in healthcare is most suitable for low-volume production, eliminating the need for costly tooling or machining processes and reducing overall waste, leading to cost-effectiveness.
4. Sterilizable Materials for Medical Applications: Given the critical application of some medical parts, the sterilizability of materials is a crucial property. 3D printing offers a range of materials, with PEEK and Ultem standing out as particularly suitable due to their strength, lightweight nature, and sterilizability. This ensures that medical devices produced through 3D printing adhere to the highest standards of hygiene.
5. Complex Design Capabilities: Unlike conventional manufacturing methods, 3D printing excels in creating complex, organic shapes. The limitless design possibilities provided by 3D printing open doors to innovations in creating body parts with improved strength and lightweight properties. By selecting the right materials and combining them with precise designs, patients experience enhanced quality, comfort, and freedom in their medical interventions.
Ensuring Safety in 3D Printing for Medicine and Healthcare: A Comprehensive Overview
The safety of 3D printing technology within the realms of medicine and healthcare is contingent upon several crucial factors, encompassing the materials employed, product design intricacies, and the intricacies of the production process. In broad strokes, 3D printing technology is deemed safe when utilized appropriately and adhering to established guidelines and standards. This entails that medical devices manufactured through 3D printing must uphold identical safety and efficacy standards as those produced through traditional manufacturing methods. However, several potential safety concerns are associated with 3D printing in the medical and healthcare domains. These include the risk of contamination if the printing process lacks proper control or if the materials used are not sterile. Additionally, there exists a potential risk of mechanical failure if the product is not meticulously designed and produced.



